In this post, we learn how to add two images of different sizes using OpenCV Python. We take two images of different sizes and perform pixel wise addition of these images. We use OpenCV Python method such as cv2.add(), cv2.addWeighted(), etc. to perform the operation.
 |
| Different Output Images after Adding Two Images |
We will cover the contents listed in the following Table of Content.
Table of Content:
- Import Required Libraries
- Load and Visualize the Images
- Create ROI
- Get height and width of images
- Find minimum height and width of images
- Crop images with minimum height and width
- Create ROI by adding Cropped Images
- Add Images
- Complete Program 1 (add images of different sizes)
- FAQs
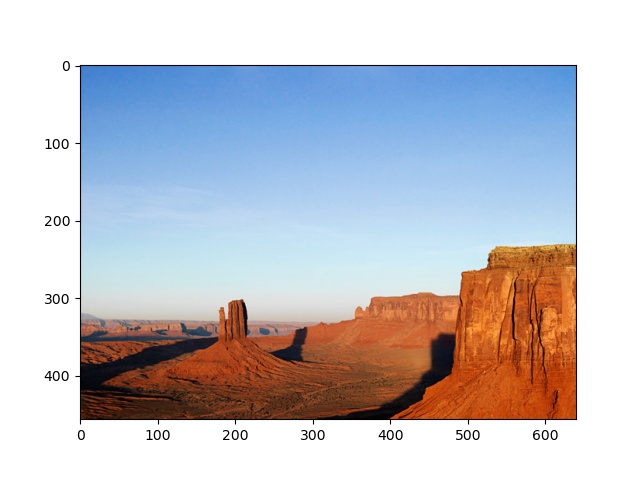
We will be using the following two images as the inputs to the programs discussed in this post.
 |
| Desert.jpg |
 |
| Penguins.jpg |
Prerequisites
- Python 3
- OpenCV
- NumPy
- Matplotlib (Optional)
Import Required Libraries/ Packages
The first step of any python programming is importing the required packages and libraries. We import the OpenCV (cv2) and Matplotlib. Using Matplotlib is optional. We used this to display the images with width and height.
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Load and Visualize the Images
The next step is to load the images. We load to images "Desert.jpg" and "Penguins.jpg". You can download the images and follow the process with the same images
Here you should change the image path accordingly.
# Load the input imagesNow we should visualize the loaded image to make sure, we have loaded correct image. This part is optional.
img1 = cv2.imread('Desert.jpg')
img2 = cv2.imread('Penguins.jpg')
# Visualize the first imageHere we used OpenCV to display/ visualize the images.
cv2.imshow('added image',img1)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
To Visualize using Matplotlib follow the below two steps. Fist step is to convert images from BGR to RGB format and then visualize.
# Convert them from BGR to RGBNow visualize first image- Desert.jpg
img1 = cv2.cvtColor(img1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
img2 = cv2.cvtColor(img2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# Visualize First Image
plt.imshow(img1)
plt.show()
 |
| Output- Desert.jpg |
# Visualize Second Image
plt.imshow(img2)
plt.show()
 |
| Output -Penguins.jpg |
We have discussed different ways to load image in Python in our previous post.
Create ROI
The main task while adding or subtracting the images of different sizes is to find the ROI (Region Of Interest). Here our main aim is to find the minimum height and width from both the images. So that we can add the common area.
Get height and width of images
First find the height and width of the images.
# Get height and width of first imageOutput
height1, width1 = img1.shape[0],img1.shape[1]
print(height1, width1)
768 1024
# Get height and width of the second image
height2, width2 = img2.shape[0],img2.shape[1]
print(height2, width2)
457 640
Notice the two images have different sizes (height and width).
Find minimum height and width of images
Now find the minimum height and width of the images.
# Find the minimum height and width of the two imagesOutput
min_height = min(height1, height2)
min_width = min(width1, width2)
print(min_height, min_width)
457 640
Crop images with minimum height and width
Crop both images with the above calculated minimum height and width.
# Crop images with minimum height and widthNow visualize the cropped images
img11 = img1[0:min_height, 0:min_width]
img22 = img2[0:min_height, 0:min_width]
# Visualize first cropped imageOutput:
plt.imshow(img11)
plt.show()
 |
| Cropped image (Desert.jpg) with min height and width |
Visualize second cropped image.
plt.imshow(img22)Output:
plt.show()
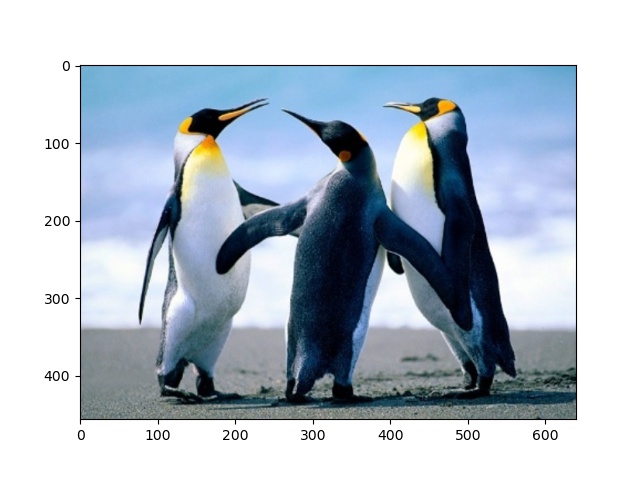 |
| Cropped image (Penguins.jpg) with min height and width |
Now the both images have the same height and width. We could now add these images.
Note: You can OpenCV to visualize the output images. We are using the Matplotlib to show the scale for height and width.
Create ROI by adding Cropped Images
Now add the cropped images with minimum height and width. This will be our ROI. We can use cv2.add() method to add the images of same size.
# Creatte ROI by adding the cropped imagesOutput:
img_add = cv2.add(img11, img22)
# Show the added miminum images
plt.imshow(img_add)
plt.show()
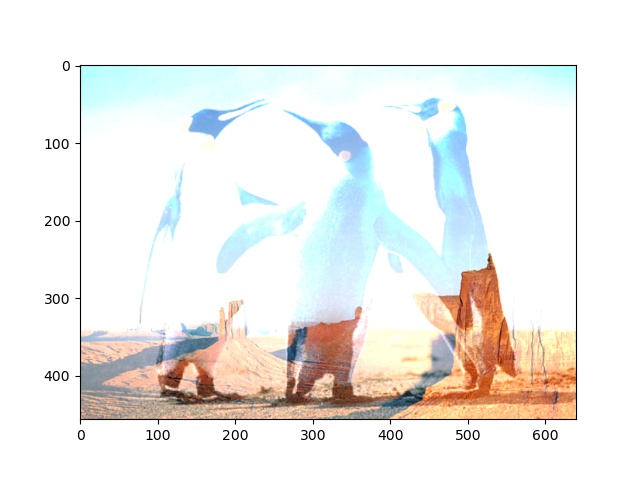 |
| ROI-image of min height and width |
Alternatively you can use cv2.addWeighted() to add the images with different weights of images.
# Add minimum images with different weightsWe have added the common part of images. We can add this image part to the original images to find the final added images.
img_add = cv2.addWeighted(img11, 0.3, img22, 0.7, 0)
plt.imshow(img_add)
plt.show()
Add Images
Let's now move to the final task to add the images. We add the cropped ROI to the original images.
Finally add ROI to original Images
Using the indexing and slicing we add the ROI to the original images.
img1[0:min_height,0:min_width] = img_add
img2[0:min_height,0:min_width] = img_add
We have added the images. Notice the second image is added in the top-left part of the first image. Can you find the reason of this?
Can you add the second image image in bottom- right part of the first image or any other part?
For these questions look at FAQs at the end of the post.
See how the second image looks after adding.
plt.imshow(img2)Output:
plt.show()
Complete Program 1 (add images of different sizes)
Now look at the complete program to add images of different size using OpenCV Python. The program describes the steps above discussed.
# import required libraries
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Read two images
img1 = cv2.imread('Desert.jpg')
img2 = cv2.imread('Penguins.jpg')
def add_images(img1, img2):
height1, width1 = img1.shape[0],img1.shape[1]
height2, width2 = img2.shape[0],img2.shape[1]
min_height = min(height1, height2)
min_width = min(width1, width2)
img11 = img1[0:min_height, 0:min_width]
img22 = img2[0:min_height, 0:min_width]
img_add = cv2.add(img11, img22)
img1[0:min_height,0:min_width] = img_add
return img1
img_add_result = add_images(img1, img2)
# cv2.imshow('added image',img_add_result)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# Convert the image from BGR to RGB
img_add_result = cv2.cvtColor(img_add_result, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
plt.imshow(img_add_result)
plt.show()
Finally we have completed all our task listed in the Table of Contents.
Now look at some FAQS
FAQs
Q1. How to add smaller image at bottom-right part of bigger image.
Answer:
Please make changes in the step- Finally add ROI to original Images. You can make indexing and slicing accordingly. Have a look at below code snippet.
img1[height1-min_height: height1, width1-min_width:width1] = img_sub
You can add this modified line in the complete program 1 and see how the output looks like.
# import required libraries
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Read two images
img1 = cv2.imread('Desert.jpg')
img2 = cv2.imread('Penguins.jpg')
def subtract_images(img1, img2):
height1, width1 = img1.shape[0],img1.shape[1]
height2, width2 = img2.shape[0],img2.shape[1]
min_height = min(height1, height2)
min_width = min(width1, width2)
img11 = img1[0:min_height, 0:min_width]
img22 = img2[0:min_height, 0:min_width]
img_sub = cv2.subtract(img11, img22)
img1[height1-min_height: height1, width1-min_width:width1] = img_sub
return img1
img_sub_result = subtract_images(img1, img2)
cv2.imshow('Subtracted image',img_sub_result)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# Convert the image from BGR to RGB
img_add_result = cv2.cvtColor(img_sub_result, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
plt.imshow(img_add_result)
plt.show()
Output:
Q2. How to add smaller image at bottom-left part of bigger image.
Answer:
As in the first Question, please make changes in the step- Finally add ROI to original Images. You can make indexing and slicing accordingly. Have a look at below code snippet.
img1[height1-min_height: height1, 0:min_width] = img_sub
You can add this modified line in the complete program 1 and see how the output looks like.
Q3. How to add smaller image at left-bottom part of bigger image.
Answer:
As in the first Question, please make changes in the step- Finally add ROI to original Images. You can make indexing and slicing accordingly. Have a look at below code snippet.
img1[0:min_height, width1-min_width:width1] = img_sub
You can add this modified line in the complete program 1 and see how the output looks like.
Advertisements





Comments
Post a Comment