In this post we discuss the method to normalize a PyTorch Tensor (both a normal tensor and an image tensor) to 0 mean and 1 variance. Why should we normalize a tensor? The normalization helps get the the tensor data within a range and it also reduces the skewness which helps in learning fast. To normalize an image in PyTorch, we read/ load image using Pillow, and then transform the image into a PyTorch Tensor using transforms.ToTensor(). Now this tensor is normalized using transforms.Normalize().
We take below image as our input image to normalize.
 |
| Image: Lena |
Table of Contents:
- Create a PyTorch Tensor
- Calculate mean, std and variance of the Tensor
- Normalize the Tensor
- Verify 0 mean and 1 variance
Create a PyTorch Tensor
We have discussed in details how to create a PyTorch Tensor in the below article.
How to Create a Tensor in PyTorch
We create a tensor of random numbers using torch.randn().
import torcha = torch.randn(3,4)print(a)
Output:
Lets take the input image and convert it into a PyTorch Tensor.
from PIL import Imagefrom torchvision import transformsimage_path = "lena.png"# read image using PILimage = Image.open(image_path)# define transform to convert PIL image# to PyTorch Tensortransform = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor()])# convert PIL image to PyTorch Tensorimg_tens = transform(image)print("Shape of Image Tensor:\n",img_tens.shape)print("Image Tensor:\n",img_tens)
Output:
The shape of the tensor after converting the image into PyTorch Tensor is (3,512,512). First 512x512 = 262144 entries are for Red, next 262144 entries are for Green, and last 262144 for Blue channels. So we need to take mean, std, and variance for these three channels RGB.
Calculate mean, std, and variance of the Tensor
We calculate mean, std, and variance of the tensor using torch.mean(), torch.std(), and torch.var().
import torch# compute mean, std, and variance of tensor "a"# created abovem = torch.mean(a)std = torch.std(a)var = torch.var(a)print("mean, std, var of tensor:\n", m, std, var)
Output:
Now we calculate the mean, std, and variance of the image tensor.
import torch# compute mean, std, and variance of image tensor# "img_tens" separatly for RGBm_img = torch.mean(img_tens,[1,2])std_img = torch.std(img_tens,[1,2])var_img = torch.var(img_tens,[1,2])print("mean, std, var of image tensor:")print("mean:", m_img)print("std:", std_img)print("var:", var_img)
Output:
You may be interested in below related article
Normalize the Tensor
Now we normalize the tensor using the formula x = (x-m)/std
# normalize the tensor "a" created above# using mean and std calculated abovea = (a-m)/std
Also normalize the image tensor using transforms.Normalize(mean, std)
from torchvision import transformsnormalize = transforms.Normalize(m_img, std_img)# normalize the image tensornor_img = normalize(img_tens)
Verify 0 mean and 1 variance
Now its time to verify that our tensor normalized to 0 mean and 1 variance.
print("Normalized tensor")print("Mean:",torch.mean(a))print("std:",torch.std(a))print("Var:",torch.var(a))
Output:
Yes!!!! Our Tensor is normalized to 0 mean and 1 variance.
Now its time to verify Image Tensor.
print("Normalized Image")print("Mean:",torch.mean(nor_img,[1,2]))print("std:",torch.std(nor_img,[1,2]))print("Var:",torch.var(nor_img,[1,2]))
Output:
Yes!!!! Our Image Tensor is also normalized to 0 mean and 1 variance.
FAQ:
Q: How do we normalize image tensor without calculated mean and standard deviation?
A. We can use mean=[0.5, 0.5, 0.5] and std =[0.5, 0.5, 0.5]. Or we cal also use the mean and std of ImageNet dataset ie mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406] and std =[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
normalize = transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.5, 0.5, 0.5],std=[0.5, 0.5, 0.5])# also we can normalize using ImageNet mean and stdnormalize = transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
Further Readings:
- How to compute mean, standard deviation and variance of a tensor in PyTorch
- How to calculate mean and standard deviation of images in PyTorch
- Mathematical Operations On Images Using OpenCV and NumPy in Python
- Basic Operations on Images using OpenCV in Python
- Different ways to load images in Python
- How to compute mean, standard deviation, and variance of a tensor in PyTorch
- How to calculate mean and standard deviation of images in PyTorch
- How to normalize image dataset in PyTorch
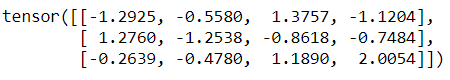





Comments
Post a Comment