PyTorch is a machine learning framework developed at Facebook's AI Research Lab. It is used in many applications such as computer vision, natural language processing. A PyTorch Tensor is basically same as NumPy array. It is a multidimensional matrix that contains elements of a single data type. A PyTorch Tensor may be one, two or multidimensional. The difference between the NumPy array and PyTorch Tensor is that the PyTorch Tensor can run on the CPU or GPU.
 |
| Image Source: https://pytorch.org/ |
Table of Contents:
Creating a PyTorch Tensor
To define a PyTorch Tensor we use torch.tensor() when we use the array or list to create the tensor. Or we can also define a random number tensor using torch.rand(), torch.randn() or torch.randint().
torch.tensor() --> to generate a tensor using numpy array or listtorch.rand() --> to generate a tensor of random numbers froma uniform distribution of interval [0,1)torch.randn() --> to generate a tensor of random numbers froma normal distributiontroch.randint() --> to generate a tensor of random integers uniformally
A PyTorch Tensor can be defined using Python List or numpy array using torch.tensor() constructor.
torch.tensor([[2.,1.], [3.,4.]])torch.tensor(np.array([[1,2,3],[9,0,2]]))
Lets have a look on the complete Python program to define 1-D PyTorch Tensor.
import torchimport numpy as np#define a PyTorch Tensor using Python Lista = torch.tensor([2.,1.,4.,3,4])print(a)# define a PyTorch Tensor using numpy arrayb = torch.tensor(np.array([1,2,3,4,5]))print(b)
Output:
Lets have a look on the complete Python program to define 2-D PyTorch Tensor.
import torchimport numpy as np#define a PyTorch Tensor using Python Lista = torch.tensor([[2.,1.,4.], [3.,4.,3],[6,4,3]])print(a)# define a PyTorch Tensor using numpy arrayb = torch.tensor(np.array([[1,2,3],[9,0,2],[2,3,1]]))print(b)
Output:
import torchprint(torch.rand(4))print(torch.randn(4))print(torch.randint(7,(1,4)))
Output:
Lets generate some 2-D PyTorch Tensor or random numbers.
import torchprint(torch.rand(3,4))print(torch.randn(3,4))print(torch.randint(7,(3,4)))
Output:
Creating a PyTorch Tensor with requires_grad=True
# Python 3 program to create a tenor with# requires_grad = Trueimport torchimport numpy as np# take a 4x4 numpy array of random numbersmat = np.random.randn(4,4)# create tnesorx = torch.tensor(mat, requires_grad = True)print(x)
 |
| Fig: PyTorch Tensor with requires_grad=True |
# define a functionout = x.pow(2).sum()# backward passout.backward()# print gradientsprint(x.grad)
Output:
 |
| Fig: PyTorch Tensor of gradients |
FAQ:
Q. How to Access and Modify contents of a PyTorch Tensor?
A.The contents of a PyTorch Tensor can be accessed and modified using the Python indexing and slicing. See the below Python snippet.
import torcha = torch.tensor([[1,2,3,4],[3,2,5,2]])# access the contentprint(a[1])print(a[1][1])# modify the contentsa[0][0] = -1print(a)
Output:
 |
Next Post: How to normalize a tensor to 0 mean and 1 variance in PyTorch
Previous Post: How to Load, Pre-process and Visualize CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 datasets in Python
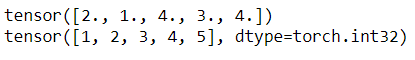



Comments
Post a Comment